difference between hv and lv | lv and hv in transformer difference between hv and lv For that, you first need to disconnect the supply voltage given to the transformer . LV Louis Vuitton Fabric Cotton100% (6801) $ 5.00 – $ 145.00. Color. Size. Clear. Add to cart. Add to wishlist. SKU: N/A Category: Cotton Fabric 100% Tags: face mask cotton100, face mask fabric, Louis Vuitton fabric, louis vuitton fabric by the yard, louis vuitton fabric cotton, louis vuitton fabric wholesale, LV by the yard, LV cotton100, LV .
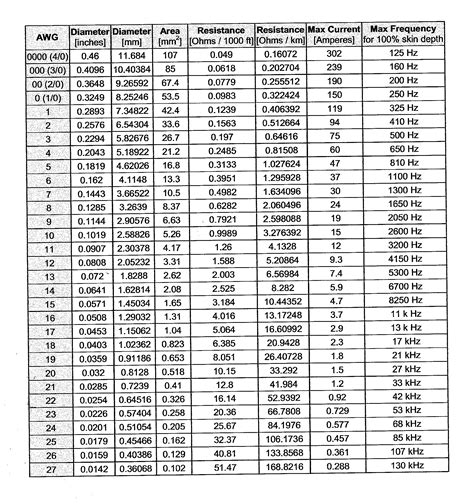
0 · voltage rating chart
1 · lv vs hv electrical
2 · lv vs hv cable
3 · lv mv hv voltage ranges
4 · lv and mv switchgear
5 · lv and hv in transformer
6 · hv vs lv distribution
7 · difference between hv and lv cable
1 runā par šo
In this post, we will learn some basic differences between two widely used electrical cables – HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage).
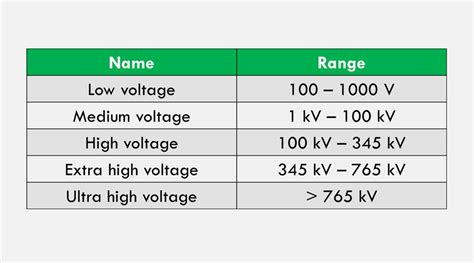
For that, you first need to disconnect the supply voltage given to the transformer . The differences between low, medium, and high voltage are stark. Low voltage systems are suitable for general consumer use, offering safety and energy efficiency. Medium .In this blog, we present the definition of LV, MV and HV, the differences between voltages and their usage areas and more for you. What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage?High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a .
When it comes to electrical systems, understanding the difference between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables is crucial. Both cables play significant roles in power distribution and . For example, high voltage is excellent for powering large devices, while low voltage is better suited for smaller ones. This is one of the key differences between high and low voltage. In this guide, we’ll break down the .
Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage. This article . In a low-voltage (LV) plastic-sheathed cable with conductor cross-sections of up to 10 mm2 per conductor or in high-voltage (HV) cables (Figure 2), the lion’s share of the cross .
The primary distinction between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables lies in their construction and insulation properties. High-voltage cables are designed with multiple .
In this post, we will learn some basic differences between two widely used electrical cables – HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage). The differences between low, medium, and high voltage are stark. Low voltage systems are suitable for general consumer use, offering safety and energy efficiency. Medium voltage systems offer a balance of power and safety, .LV cables are low voltage cables that are designed to transmit electrical power at voltage levels up to 1000 V. They are typically used for short-distance power transmission and distribution, such as within buildings and homes. In contrast, HV cables are high and medium-voltage cables that are designed to transmit electrical power at voltage .
In this blog, we present the definition of LV, MV and HV, the differences between voltages and their usage areas and more for you. What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage?High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.When it comes to electrical systems, understanding the difference between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables is crucial. Both cables play significant roles in power distribution and transmission, but they have different purposes and distinct characteristics. For example, high voltage is excellent for powering large devices, while low voltage is better suited for smaller ones. This is one of the key differences between high and low voltage. In this guide, we’ll break down the pros and cons of .
Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage. This article explores these classifications and their applications, highlighting their differences and relevant products from Blue Jay. In a low-voltage (LV) plastic-sheathed cable with conductor cross-sections of up to 10 mm2 per conductor or in high-voltage (HV) cables (Figure 2), the lion’s share of the cross-sectional area is occupied by the insulating material. The primary distinction between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables lies in their construction and insulation properties. High-voltage cables are designed with multiple semiconductor and shielding layers, which significantly exceed the .In this post, we will learn some basic differences between two widely used electrical cables – HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage).
The differences between low, medium, and high voltage are stark. Low voltage systems are suitable for general consumer use, offering safety and energy efficiency. Medium voltage systems offer a balance of power and safety, .LV cables are low voltage cables that are designed to transmit electrical power at voltage levels up to 1000 V. They are typically used for short-distance power transmission and distribution, such as within buildings and homes. In contrast, HV cables are high and medium-voltage cables that are designed to transmit electrical power at voltage .
In this blog, we present the definition of LV, MV and HV, the differences between voltages and their usage areas and more for you. What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage?High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.When it comes to electrical systems, understanding the difference between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables is crucial. Both cables play significant roles in power distribution and transmission, but they have different purposes and distinct characteristics. For example, high voltage is excellent for powering large devices, while low voltage is better suited for smaller ones. This is one of the key differences between high and low voltage. In this guide, we’ll break down the pros and cons of .

Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage. This article explores these classifications and their applications, highlighting their differences and relevant products from Blue Jay.
voltage rating chart
In a low-voltage (LV) plastic-sheathed cable with conductor cross-sections of up to 10 mm2 per conductor or in high-voltage (HV) cables (Figure 2), the lion’s share of the cross-sectional area is occupied by the insulating material.

louis vuitton supreme rucksack
The best online hub for the latest Formula 1 news, results, photos, videos, (live)standings and other great content!
difference between hv and lv|lv and hv in transformer