lv apex | Lv apex aneurysm lv apex The left ventricle (LV) is affected by many diseases with different clinical and . $5,400.00
0 · trabeculated Lv apex
1 · severe hypokinesis of the apex
2 · hypokinesis of the apex
3 · false tendon in Lv apex
4 · cardiac apex location
5 · Lv apex thrombus
6 · Lv apex blood supply
7 · Lv apex aneurysm
$5,850.00

The apex of the left ventricle is a potential entry sight into the left ventricle for valve therapies. .
The 17 segments of the left ventricle. These 17 segments can be arranged as a polar (bull’s-eye) plot with the apex in the center, the four apical segments as . Background Left ventricular (LV) twist has been defined as the counterclockwise rotation of the ventricular apex with respect to the base .
The left ventricular apex is difficult to visualize, particularly in patients with a dilated left .
The left ventricle (LV) is affected by many diseases with different clinical and . The apex of the heart is the very tip and helps pump or “wring out” blood from the ventricles to the rest of the body (LV apex) or the lungs (RV apex). It does this by helping regulate.The apex of the left ventricle is a potential entry sight into the left ventricle for valve therapies. Left ventricular assist devices can utilize the apex as a place to sew in blood conduits to fill the device with blood.The 17 segments of the left ventricle. These 17 segments can be arranged as a polar (bull’s-eye) plot with the apex in the center, the four apical segments as the first ring, the six mid-cavity segments as the second ring, and the six basal segments as the outer ring (Figure 2). Figure 2.
Background Left ventricular (LV) twist has been defined as the counterclockwise rotation of the ventricular apex with respect to the base during systole. We recently showed that, since base rotation is minimal, measurement of apex rotation reflects the dynamics of LV twist.The left ventricular apex is difficult to visualize, particularly in patients with a dilated left ventricle. In addition to retroflexion, rightward flexion can often be helpful to minimize foreshortening of the left ventricle. Far-field imaging can be improved by decreasing the transmission frequency or by using harmonic imaging.
The left ventricle (LV) is affected by many diseases with different clinical and morphological features. Within this broad spectrum, a subset of heterogeneous diseases is characterised as preferentially affecting the LV apex.
trabeculated Lv apex
severe hypokinesis of the apex
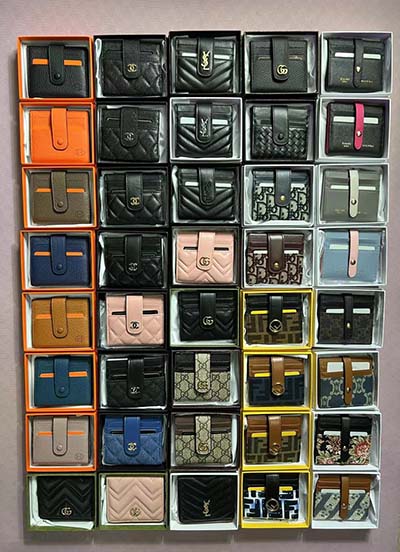
gucci duffle bag women's
Apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (ApHCM) is a unique disease with pathologic hypertrophy mainly at the left ventricular (LV) apex. Although previous studies have indicated apical dysfunction in ApHCM, how apical mechanics change during disease progression has not been thoroughly examined. To obtain LV twist mechanics using 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography, we need 2 short-axis views from the LV base and apex. Data obtained from these views are postprocessed with dedicated software packages to construct LV twist mechanics curves characterizing the entire cardiac cycle. Increased age, lower left ventricular ejection fraction, and noncompaction extending beyond the left ventricular apex to the midbasal segments was associated with increased mortality among patients with LVNC.
The left ventricular apex is considered a versatile access site since it is easily accessible through left lateral mini-thoracotomy and provides direct antegrade access to the aortic as well as retrograde access to the mitral valve. The apex of the heart is the very tip and helps pump or “wring out” blood from the ventricles to the rest of the body (LV apex) or the lungs (RV apex). It does this by helping regulate.The apex of the left ventricle is a potential entry sight into the left ventricle for valve therapies. Left ventricular assist devices can utilize the apex as a place to sew in blood conduits to fill the device with blood.
The 17 segments of the left ventricle. These 17 segments can be arranged as a polar (bull’s-eye) plot with the apex in the center, the four apical segments as the first ring, the six mid-cavity segments as the second ring, and the six basal segments as the outer ring (Figure 2). Figure 2. Background Left ventricular (LV) twist has been defined as the counterclockwise rotation of the ventricular apex with respect to the base during systole. We recently showed that, since base rotation is minimal, measurement of apex rotation reflects the dynamics of LV twist.
The left ventricular apex is difficult to visualize, particularly in patients with a dilated left ventricle. In addition to retroflexion, rightward flexion can often be helpful to minimize foreshortening of the left ventricle. Far-field imaging can be improved by decreasing the transmission frequency or by using harmonic imaging.
The left ventricle (LV) is affected by many diseases with different clinical and morphological features. Within this broad spectrum, a subset of heterogeneous diseases is characterised as preferentially affecting the LV apex. Apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (ApHCM) is a unique disease with pathologic hypertrophy mainly at the left ventricular (LV) apex. Although previous studies have indicated apical dysfunction in ApHCM, how apical mechanics change during disease progression has not been thoroughly examined. To obtain LV twist mechanics using 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography, we need 2 short-axis views from the LV base and apex. Data obtained from these views are postprocessed with dedicated software packages to construct LV twist mechanics curves characterizing the entire cardiac cycle.
Increased age, lower left ventricular ejection fraction, and noncompaction extending beyond the left ventricular apex to the midbasal segments was associated with increased mortality among patients with LVNC.
gucci duffle bag large
hypokinesis of the apex
$799.00
lv apex|Lv apex aneurysm